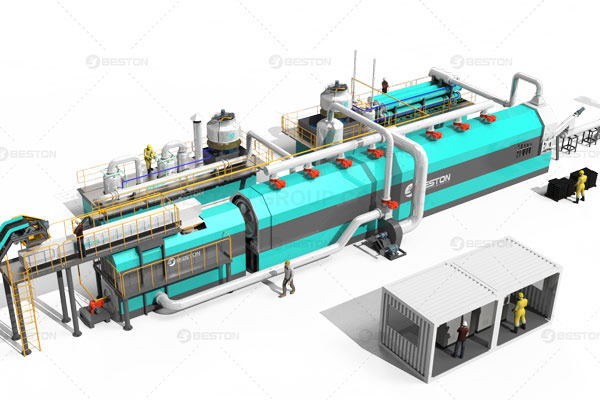
Plastic waste has become one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. With global plastic production exceeding 380 million tons annually, the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans has raised serious ecological concerns. Conventional recycling methods often fail to manage this growing problem efficiently, which has led researchers to explore alternative solutions such as pyrolysis.
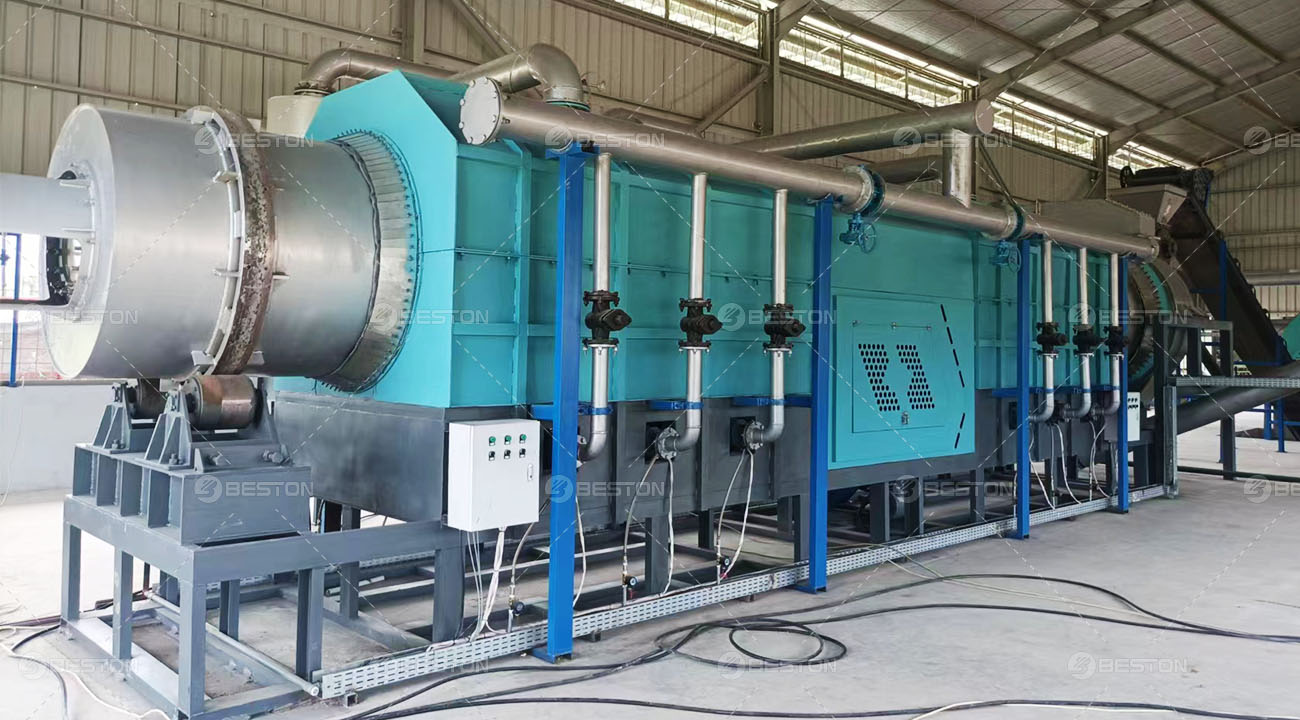
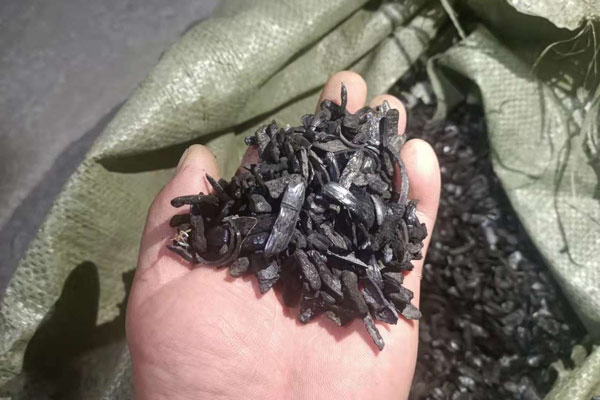
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition process in which organic materials, like plastics, are heated in the absence of oxygen, breaking down into smaller molecules. This process produces pyrolysis oil, gases, and char. Among these products, pyrolysis oil is particularly valuable, as it can be refined into fuels or chemicals, offering both economic and environmental benefits. However, traditional pyrolysis methods often yield oil of inconsistent quality, containing a mixture of hydrocarbons with varying chain lengths, oxygenates, and undesirable impurities.

The Role of Catalysts in Pyrolysis
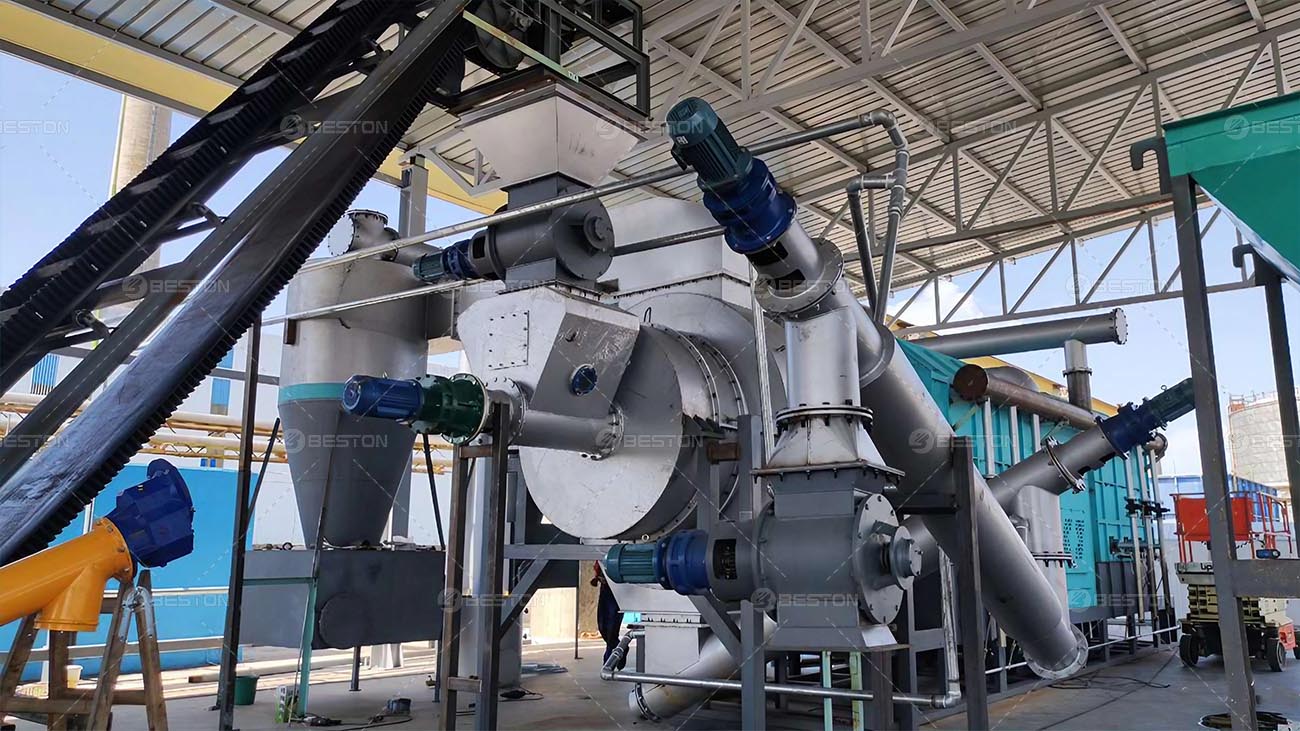
This is where catalytic pyrolysis comes into play. Catalysts are substances that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. In the context of plastic pyrolysis, catalysts can significantly influence the composition, yield, and quality of the resulting pyrolysis oil. By promoting specific reaction pathways, catalysts help break down long-chain polymers into more uniform hydrocarbons, reduce the formation of heavy residues, and enhance the overall efficiency of the process.
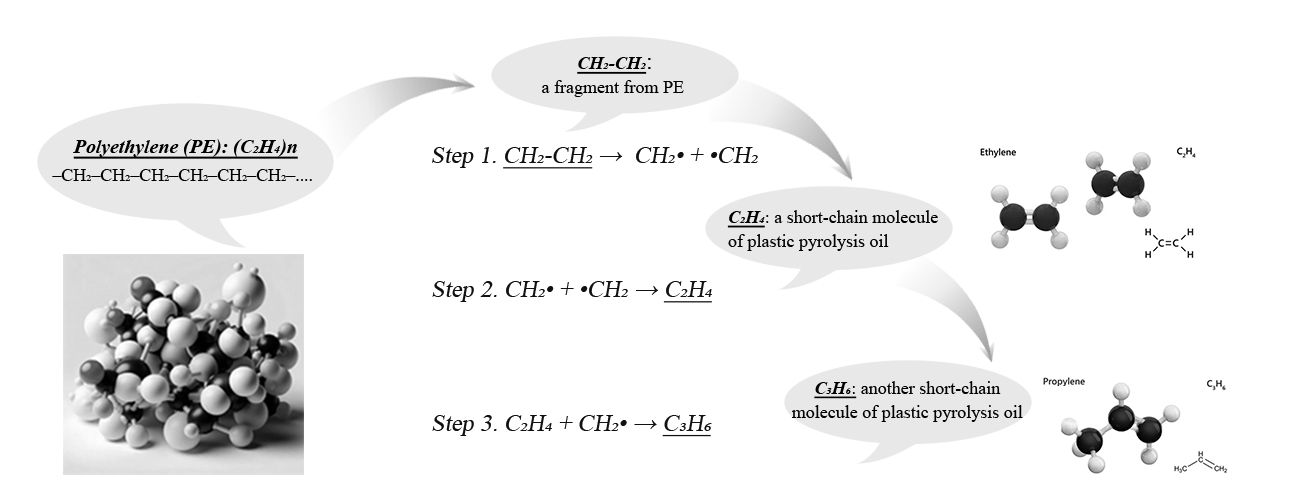
Common catalysts used in plastic pyrolysis equipment include zeolites, mesoporous materials, and metal oxides. Zeolites, for example, have a highly porous structure and acidic sites that facilitate cracking reactions, converting high-molecular-weight polymers into lighter hydrocarbons suitable for fuel applications. Metal oxides, on the other hand, can promote deoxygenation reactions, improving the stability and energy content of the pyrolysis oil.
Benefits of Catalytic Pyrolysis
The integration of catalysts in the plastic pyrolysis process offers several advantages:
- Improved Oil Quality: Catalysts help produce oil with a higher proportion of desirable hydrocarbons, such as gasoline and diesel-range molecules, reducing the need for extensive refining.
- Higher Yield: By guiding the reaction pathways, catalysts can increase the total liquid yield, making the process more economically viable.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Catalytic pyrolysis can minimize the formation of tar and char residues, lowering the potential for waste generation and emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Some catalysts allow pyrolysis to occur at lower temperatures, reducing the overall energy consumption of the process.
Industrial Applications and Future Prospects
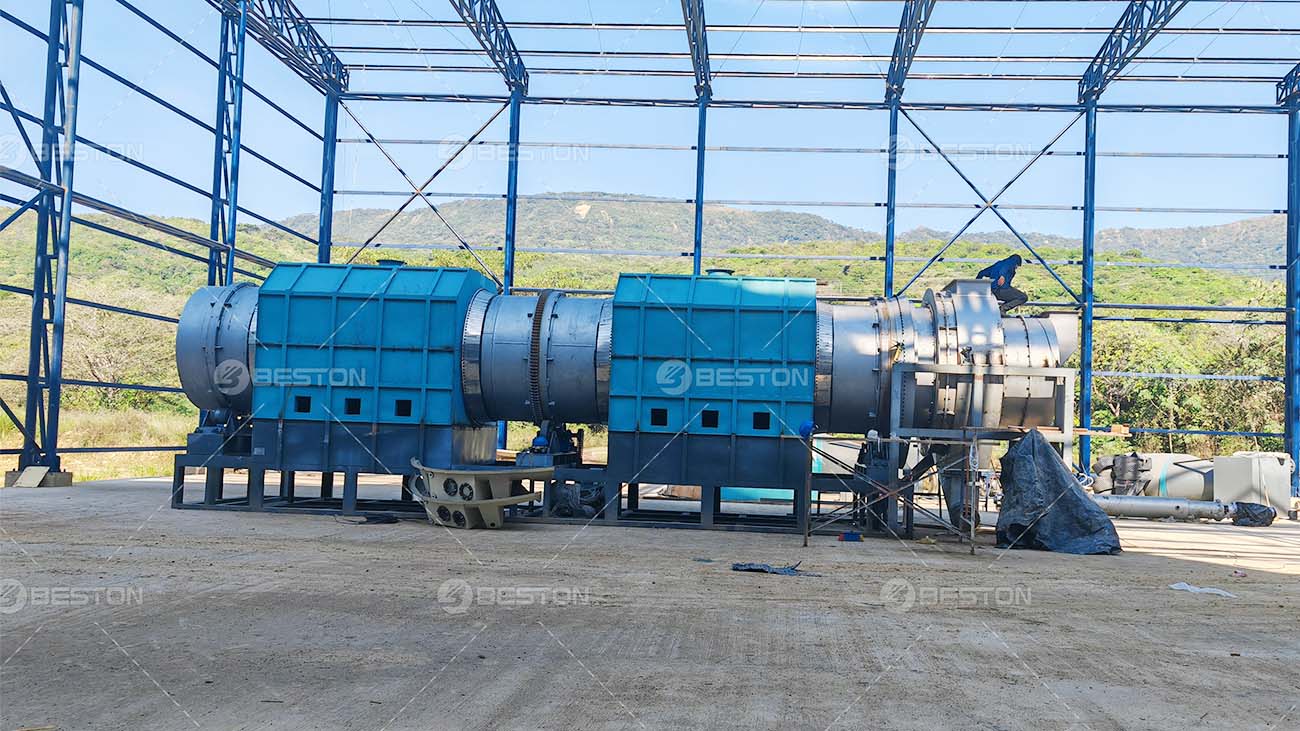
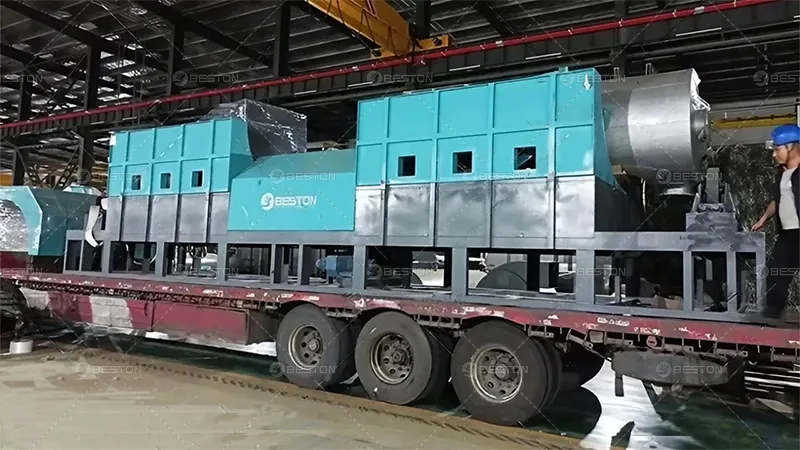
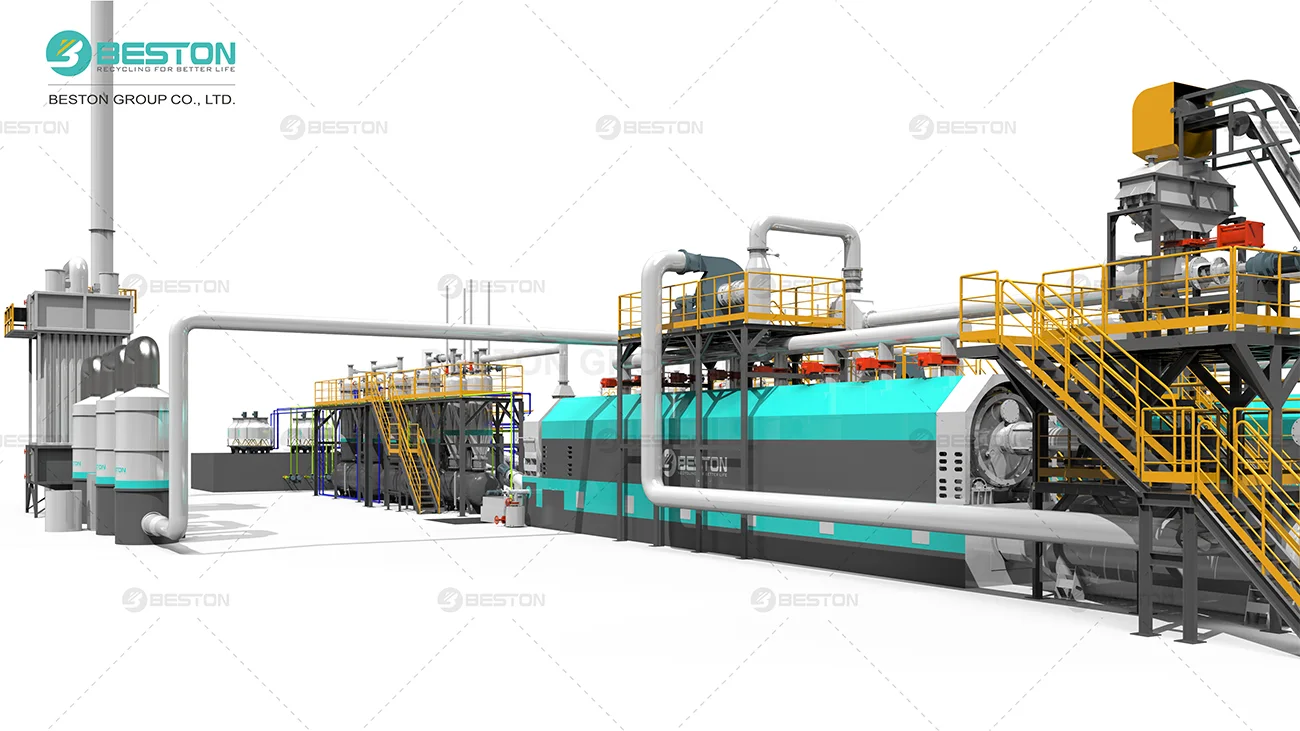
Catalytic pyrolysis has begun to attract interest from both the waste management and energy sectors. Industrial-scale pilot projects on catalytic processes have demonstrated the potential of converting mixed plastic waste into valuable liquid fuels using plastic into fuel machine. These innovations could provide a sustainable pathway for managing plastic pollution while producing renewable energy resources.
Conclusion
Catalytic pyrolysis represents a significant advancement in the field of plastic waste conversion. By enhancing the yield and quality of pyrolysis oil, catalysts offer a practical and efficient solution to the growing plastic pollution crisis. As research and industrial adoption continue, this technology could play a crucial role in creating a more sustainable and circular economy, turning what was once considered waste into a valuable resource. Beston Group – an industry expert who hold patents for catalytic pyrolysis technology.